XT Boot Loader
XTLDR (abbreviation of XT Loader) is the boot loader dedicated for XTOS. It is the first program launched by the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) of the computer and is responsible for loading the rest of ExectOS. The procedure is quite different for UEFI and BIOS systems. However currently, legacy BIOS boot procedure is not supported by ExectOS.
UEFI
The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) has support for reading both the partition table as well as file systems. UEFI does not launch any boot code from the Master Boot Record (MBR) whether it exists or not, instead booting relies on boot entries in the NVRAM. The UEFI specification mandates support for the FAT12, FAT16, and FAT32 file systems, as well as ISO9660 for optical discs. Any conformant vendor can optionally add support for additional file systems.
UEFI launches EFI applications, e.g. boot loaders, boot managers, UEFI shell, etc. These applications are usually stored as files in the EFI system partition (ESP). The applications can be launched by adding a boot entry to the NVRAM or from the UEFI shell.
Startup Process
When a PC is powered on its UEFI firmware initializes the hardware components of the system. This includes CPU, memory, and device initialization. Firmware has its own boot manager, which is responsible for loading UEFI applications stored in the EFI System Partition (ESP), a dedicated partition on a data storage device, formatted with any from the supported filesystem and attempts to load the selected EFI application (usually an OS bootloader) into memory and transfers control to it.
XTLDR accesses the file system on the ESP partition and reads the xtldr.ini file to determine what Operating Systems are present. Also additional configuration, like debugging options is loaded. Afterwards, XTLDR loads additional modules, in order to extend its functionality as well as to support additional file systems, that are normally not supported by UEFI. This allows to boot Operating System kernel from the partition other to ESP. Then boot loader menu is presented to the user.
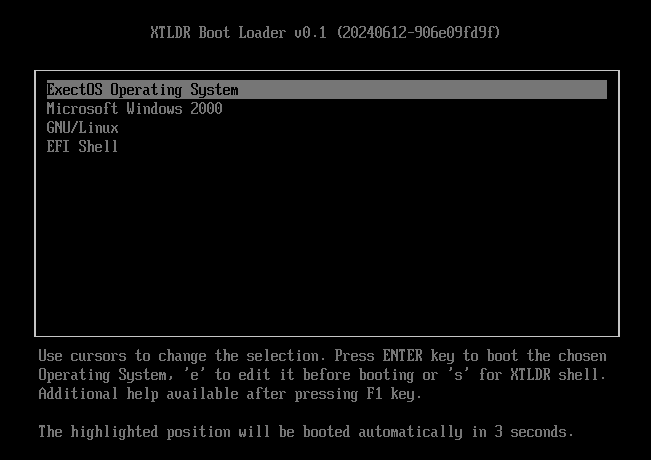
After a user choose the position from the list, or timeout exceeded, XTLDR continues with loading additional modules, specific to the chosen Operating System. If a non XTOS is selected, XTLDR loads the associated kernel file listed in the configuration file and gives it control. Otherwise, if XTOS is selected, boot loader loads registry HIVE data, kernel and boot drivers. Finally, starts the kernel, passing to it all the necessary information.
XTLDR Configuration
XTLDR’s first action is to read the xtldr.ini file. It describes whole configuration for the boot loader as well as allows the user to choose which Operating System to boot from at the menu. it also allows the user to pass preconfigured options to the kernel. Regardless an OS, the location of the Operating System is written as an ARC (Advanced RISC Computing) path. Below is an example of the xtldr.ini file:
[XTLDR]
Debug=COM1,115200
Default=ExectOS
KeepLastBoot=TRUE
Modules=beep
Timeout=10
Tune=400 880 2 988 2 783 2 392 2 587 3
[ExectOS]
SystemName="ExectOS Operating System"
SystemType=XTOS
BootModules=xtos_o
SystemPath=multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)/ExectOS
KernelFile=xtoskrnl.exe
Parameters=DEBUG=COM1,115200
A full list of configuration options with their descriptions can be found in the example configuration file in project’s GIT repository.
 ExectOS Operating System
ExectOS Operating System